Starting with version 2.3 gqrx has an option to stream the audio over UDP to a remote host. This can be used to send the audio to external data decoders or for remote monitoring. This post describes the streaming functionality in gqrx and provides a few examples for how to use it.
The streamed audio has the following specifications:
- Channels: 1 (left)
- Sample rate: 48 kHz
- Sample format: 16 bit signed, little endian (S16LE)
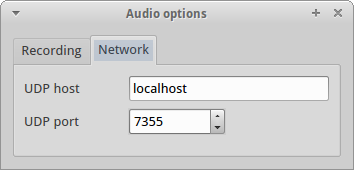
First, you must configure the network settings. This is done in the Network tab of the audio settings window:
As can be seen on the screenshot the remote host and port number are configurable. You can enter a host name or an IP address as long as it resolves.
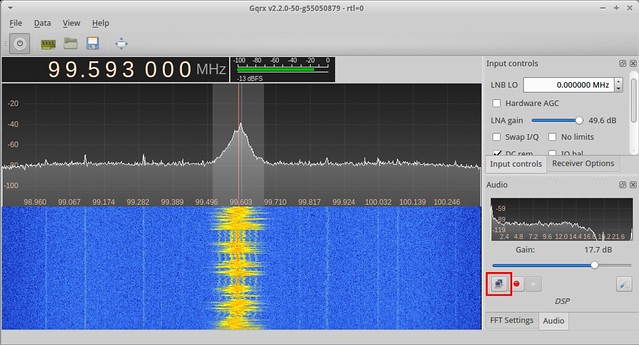
Once configured you can start streaming by simply pressing the small network button located left to the audio recording button, see the red marking on the screenshot below.
You can verify the data is coming through at the opposite end using netcat or nc:
$ nc -l -u 7355
You should see a lots of funny symbols scroll through the terminal. You can now pipe the output of netcat to other applications, see the next section for examples.
If you don’t see any output, try including the host name or IP in the command line:
$ nc -l -u localhost 7355
or
$ nc -l -u 127.0.0.1 7355
Examples
Play audio using the alsa player
The following example will send the audio to the ALSA player application:
$ nc -l -u 7355 | aplay -r 48k -f S16_LE -t raw -c 1
If you get command not found you must install the alsa-utils package.
Decode POCSAG using multimon-ng
The following command line will re-sample the raw audio to 22.05 kHz and send it to multimon-ng and decode POCSAG data (thanks to André Schmelzer for this):
$ nc -l -u 7355 | \
sox -t raw -esigned-integer -b16 -r 48000 - -esigned-integer -b16 -r 22050 -t raw - | \
multimon-ng -t raw -a SCOPE -a POCSAG512 -a POCSAG1200 -a POCSAG2400 -f alpha -
Note that the above is one command line. I just used the ‘\’ character to split one long line into multiple lines for readability.
Decode APRS using direwolf
The following command line will start Direwolf with UDP input (requires Direwolf 1.0-beta or later):
$ direwolf -r 48000 udp:7355
Streaming audio to VLC
The following command line will start VLC playing raw reading audio from the UDP socket:
$ vlc --demux=rawaud --rawaud-channels=1 --rawaud-samplerate=48000 udp://@:7355